Arduino 开发
本章节包含以下部分,请按需阅读:
Arduino 入门教程
初次接触 Arduino ESP32 开发,想要快速上手?我们为您准备了一套通用的 入门教程。
- 第0节 认识 ESP32
- 第1节 安装和配置 Arduino IDE
- 第2节 Arduino 基础知识
- 第3节 数字输出/输入
- 第4节 模拟输入
- 第5节 脉冲宽度调制 (PWM)
- 第6节 串行通信 (UART)
- 第7节 I2C 通信
- 第8节 SPI 通信
- 第9节 Wi-Fi 基础用法
- 第10节 网页服务器
- 第11节 蓝牙 (Bluetooth)
- 第12节 LVGL 图形界面开发
- 第13节 综合项目
请注意:该教程使用 ESP32-S3-Zero 作为教学示例,所有硬件代码均基于其引脚布局。在动手实践前,建议您对照手中的开发板引脚图,确认引脚配置无误。
配置开发环境
1. 安装和配置 Arduino IDE
请参考 安装和配置 Arduino IDE 教程 下载安装 Arduino IDE 并添加 ESP32 支持。
2. 安装库
要运行示例,需要安装对应的库。示例代码使用 GFX Library for Arduino 库驱动 ST7789V2 显示屏
,并使用 Arduino_DriveBus 库驱动 CST816T 触摸芯片。
可从 此链接 下载 ESP32-S3-Touch-LCD-1.69 开发板的示例程序包。包内的 Arduino\libraries 目录已包含本教程所需的全部库文件。
| 库或文件名称 | 说明 | 版本 | 安装方式 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arduino_DriveBus | CST816 触摸芯片驱动库 | v1.0.1 | 手动安装 |
| GFX Library for Arduino | ST7789 显示驱动图形库 | v1.4.9 | 通过库管理器或手动安装 |
| SensorLib | PCF85063、QMI8658 传感器驱动库 | v0.1.6 | 通过库管理器或手动安装 |
| lvgl | LVGL 图形库 | v8.4.0 | 通过库管理器或手动安装 |
| Mylibrary/pin_config.h | 开发板引脚宏定义 | —— | 手动安装 |
| lv_conf.h | LVGL 配置文件 | —— | 手动安装 |
LVGL 及其驱动库的版本之间存在较强的依赖关系。例如,为 LVGL v8 编写的驱动可能不兼容 LVGL v9。为确保示例能够稳定复现,推荐使用上表列出的特定版本。混合使用不同版本的库可能导致编译失败或运行时异常。
安装步骤:
-
解压已下载的 示例程序包。
-
将其
Arduino\libraries目录下的所有文件夹(Arduino_DriveBus、GFX_Library_for_Arduino 等)复制到 Arduino 的库文件夹中。信息Arduino 库文件夹的路径通常是:
c:\Users\<用户名>\Documents\Arduino\libraries。也可以在 Arduino IDE 中通过 文件 > 首选项,查看“项目文件夹位置”来定位。库文件夹就是此路径下的
libraries文件夹。 -
其他安装方式请参考:Arduino 库管理教程。
3. 其他提示
-
ESP32-S3-Touch-LCD-1.69 支持在 Arduino IDE 中直接选择型号。
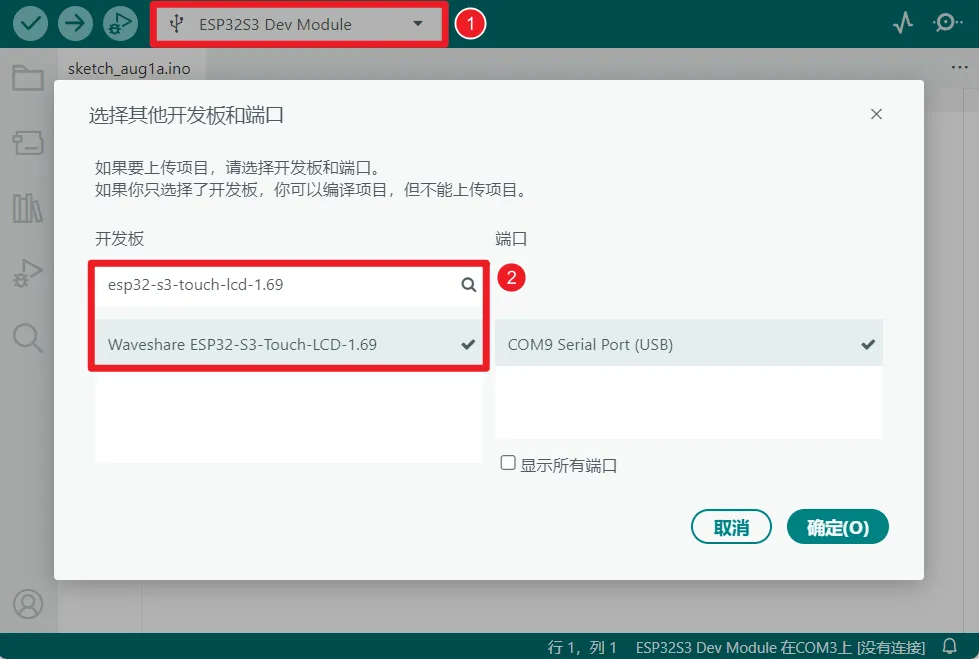
-
ESP32-S3-Touch-LCD-1.69 使用 ESP32-S3 原生 USB 接口,而非 UART 转 USB。对于串口通信:
-
printf()函数可直接使用; -
若要使用
Serial.println()函数,需要额外配置:在 IDE 工具菜单中启用"USB CDC On Boot"选项,或在代码中声明 HWCDC 对象处理 USB 串口通信。备注如下图所示,在 Arduino IDE 的"工具"选项中设置"USB CDC On Boot"
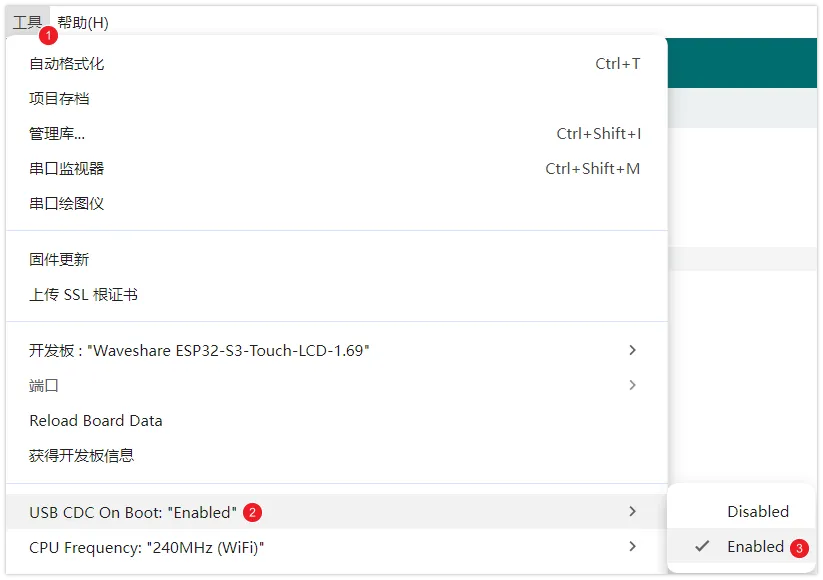
-
示例程序
Arduino 示例程序位于 示例程序包 的 Arduino/examples 目录中。
| 示例程序 | 基础例程说明 | 依赖库 |
|---|---|---|
| 01_HelloWorld | 展示基本的图形库功能,也可以用于测试显示屏的基础性能以及随机文本显示效果 | GFX_Library_for_Arduino |
| 02_Drawing_board | 展示基本的图形库功能,也可以用于测试显示屏的基础性能以及随机文本显示效果 | GFX_Library_for_Arduino,Arduino DriveBus |
| 03_GFX_AsciiTable | 根据屏幕尺寸,在显示屏上按行列打印 ASCII 字符 | GFX_Library_for_Arduino |
| 04_GFX_ESPWiFiAnalyzer | 在 ST7789 显示器上绘制 WiFi 频段信号强度 | GFX_Library_for_Arduino |
| 05_GFX_Clock | 一个简单的 ST7789 时钟示例,通过简单的标记指针和时间管理实现时钟 | GFX_Library_for_Arduino |
| 06_GFX_PCF85063_simpleTime | 显示当前时间 | SensorLib,GFX_Library_for_Arduino |
| 07_LVGL_Measuring_voltage | 板上预留分压测电压,使用 GPIO1 读取模拟量值并通过分压公式得出电池电压 | LVGL |
| 08_LVGL_PCF85063_simpleTime | 在 LVGL 下使用 PCF85063 RTC 模块在 ST7789 显示屏上显示当前时间 | LVGL,SensorLib |
| 09_LVGL_Keys_Bee | 多功能按钮使用 | LVGL |
| 10_LVGL_QMI8658_ui | 使用 LVGL 进行图形显示,与 QMI8658 IMU 通信以获取加速度计和陀螺仪数据 | LVGL,SensorLib |
| 11_LVGL_Arduino | LVGL 演示 | LVGL,Arduino DriveBus |
01_HelloWorld
本示例展示如何使用 ST7789 显示屏,结合 Arduino GFX 库和 Arduino DriveBus 库实现动态文本显示。具体来说,它在显示屏上固定位置显示文本“Hello World!”后,在循环中每隔一秒随机选择新的位置、颜色和大小再次显示这段文本。该代码也可以用于测试显示屏的基础性能。

代码
01_HelloWorld.ino
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "Arduino_GFX_Library.h"
#include "pin_config.h"
#include <Wire.h>
#include "HWCDC.h"
HWCDC USBSerial;
Arduino_DataBus *bus = new Arduino_ESP32SPI(LCD_DC, LCD_CS, LCD_SCK, LCD_MOSI);
Arduino_GFX *gfx = new Arduino_ST7789(bus, LCD_RST /* RST */,
0 /* rotation */, true /* IPS */, LCD_WIDTH, LCD_HEIGHT, 0, 20, 0, 0);
void setup(void) {
USBSerial.begin(115200);
// USBSerial.setDebugOutput(true);
// while(!USBSerial);
USBSerial.println("Arduino_GFX Hello World example");
// Init Display
if (!gfx->begin()) {
USBSerial.println("gfx->begin() failed!");
}
gfx->fillScreen(BLACK);
pinMode(LCD_BL, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LCD_BL, HIGH);
gfx->setCursor(10, 10);
gfx->setTextColor(RED);
gfx->println("Hello World!");
delay(5000); // 5 seconds
}
void loop() {
gfx->setCursor(random(gfx->width()), random(gfx->height()));
gfx->setTextColor(random(0xffff), random(0xffff));
gfx->setTextSize(random(6) /* x scale */, random(6) /* y scale */, random(2) /* pixel_margin */);
gfx->println("Hello World!");
delay(1000); // 1 second
}
代码解释
-
显示初始化 :
if (!gfx->begin()) {
USBSerial.println("gfx->begin() failed!");
} -
清屏并显示文本 :
gfx->fillScreen(BLACK);
gfx->setCursor(10, 10);
gfx->setTextColor(RED);
gfx->println("Hello World!"); -
动图显示 :
gfx->setCursor(random(gfx->width()), random(gfx->height()));
gfx->setTextColor(random(0xffff), random(0xffff));
gfx->setTextSize(random(6), random(6), random(2));
gfx->println("Hello World!");
02_Drawing_board
本示例演示如何使用 CST816T 触摸 IC 和 Arduino GFX 库在 ESP32 开发板上实现触摸交互。代码包括初始化触摸 IC 和配置显示屏。在循环部分,程序读取触摸屏的坐标信息,并在识别到触摸输入时,在屏幕上对应位置绘制一个圆点。该示例可以用于测试触摸屏的基本响应功能,并为触摸交互应用提供基础。程序启动时,它还展示了从黑暗到全亮的显示屏加载效果,使用户获得动态的视觉体验。

代码
02_Drawing_board.ino
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "pin_config.h"
#include "Arduino_GFX_Library.h"
#include "Arduino_DriveBus_Library.h"
#include "HWCDC.h"
HWCDC USBSerial;
Arduino_DataBus *bus = new Arduino_ESP32SPI(LCD_DC, LCD_CS, LCD_SCK, LCD_MOSI);
Arduino_GFX *gfx = new Arduino_ST7789(bus, LCD_RST /* RST */,
0 /* rotation */, true /* IPS */, LCD_WIDTH, LCD_HEIGHT, 0, 20, 0, 0);
std::shared_ptr<Arduino_IIC_DriveBus> IIC_Bus =
std::make_shared<Arduino_HWIIC>(IIC_SDA, IIC_SCL, &Wire);
void Arduino_IIC_Touch_Interrupt(void);
std::unique_ptr<Arduino_IIC> CST816T(new Arduino_CST816x(IIC_Bus, CST816T_DEVICE_ADDRESS,
TP_RST, TP_INT, Arduino_IIC_Touch_Interrupt));
void Arduino_IIC_Touch_Interrupt(void) {
CST816T->IIC_Interrupt_Flag = true;
}
void setup() {
USBSerial.begin(115200);
Wire.begin(IIC_SDA, IIC_SCL);
while (CST816T->begin() == false) {
USBSerial.println("CST816T initialization fail");
delay(2000);
}
USBSerial.println("CST816T initialization successfully");
CST816T->IIC_Write_Device_State(CST816T->Arduino_IIC_Touch::Device::TOUCH_DEVICE_INTERRUPT_MODE,
CST816T->Arduino_IIC_Touch::Device_Mode::TOUCH_DEVICE_INTERRUPT_PERIODIC);
gfx->begin();
pinMode(LCD_BL, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LCD_BL, HIGH);
gfx->fillScreen(WHITE);
for (int i = 0; i <= 255; i++) //0-255
{
gfx->Display_Brightness(i);
gfx->setCursor(20, 100);
gfx->setTextColor(BLUE);
gfx->setTextSize(2);
gfx->println("Loading board");
delay(3);
}
delay(500);
gfx->fillScreen(WHITE);
}
void loop() {
int32_t touchX = CST816T->IIC_Read_Device_Value(CST816T->Arduino_IIC_Touch::Value_Information::TOUCH_COORDINATE_X);
int32_t touchY = CST816T->IIC_Read_Device_Value(CST816T->Arduino_IIC_Touch::Value_Information::TOUCH_COORDINATE_Y);
USBSerial.printf("Touch X:%d Y:%d\n", touchX, touchY);
if (touchX > 20 && touchY > 20) {
gfx->fillCircle(touchX, touchY, 3, BLUE);
}
}
代码解释
-
显示屏初始化与亮度渐变动画 :
gfx->begin();
gfx->fillScreen(WHITE);
for (int i = 0; i <= 255; i++) {
gfx->Display_Brightness(i);
gfx->setCursor(30, 150);
gfx->setTextColor(BLUE);
gfx->setTextSize(4);
gfx->println("Loading board");
delay(3);
}
03_GFX_AsciiTable
本示例展示如何用 ST7789 显示屏结合 Arduino GFX 库,创建一个 ASCII 表格的显示效果。具体而言,代码初始化显示屏后,按照预定义的颜色和位置在屏幕上显示 ASCII 字符索引。首先,“Arduino_GFX AsciiTable example” 字样通过 USBSerial 打印到串口监视器,然后在屏幕上按照两种颜色(绿色和蓝色)固定显示索引,接着用白色在黑色背景上显示完整 ASCII 字符表。

代码
03_GFX_AsciiTable.ino
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "Arduino_GFX_Library.h"
#include "pin_config.h"
#include <Wire.h>
#include "HWCDC.h"
HWCDC USBSerial;
Arduino_DataBus *bus = new Arduino_ESP32SPI(LCD_DC, LCD_CS, LCD_SCK, LCD_MOSI);
Arduino_GFX *gfx = new Arduino_ST7789(bus, LCD_RST /* RST */,
0 /* rotation */, true /* IPS */, LCD_WIDTH, LCD_HEIGHT, 0, 20, 0, 0);
void setup(void) {
USBSerial.begin(115200);
// USBSerial.setDebugOutput(true);
// while(!USBSerial);
USBSerial.println("Arduino_GFX AsciiTable example");
int numCols = LCD_WIDTH / 8;
int numRows = LCD_HEIGHT / 10;
#ifdef GFX_EXTRA_PRE_INIT
GFX_EXTRA_PRE_INIT();
#endif
// Init Display
if (!gfx->begin()) {
USBSerial.println("gfx->begin() failed!");
}
gfx->fillScreen(BLACK);
pinMode(LCD_BL, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LCD_BL, HIGH);
gfx->setTextColor(GREEN);
for (int x = 0; x < numRows; x++) {
gfx->setCursor(10 + x * 8, 2);
gfx->print(x, 16);
}
gfx->setTextColor(BLUE);
for (int y = 0; y < numCols; y++) {
gfx->setCursor(2, 12 + y * 10);
gfx->print(y, 16);
}
char c = 0;
for (int y = 0; y < numRows; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < numCols; x++) {
gfx->drawChar(10 + x * 8, 12 + y * 10, c++, WHITE, BLACK);
}
}
delay(5000); // 5 seconds
}
void loop() {
}
代码解释
-
初始化显示屏 :
if (!gfx->begin()) {
USBSerial.println("gfx->begin() failed!");
} -
计算行列并标注编号 :
这里根据显示屏的尺寸计算出可以显示的列数和行数。然后分别使用两个循环,设置不同的文本颜色,在显示屏上打印出行和列的编号,以便在后续绘制 ASCII 字符时可以方便地确定字符的位置。
int numCols = LCD_WIDTH / 8;
int numRows = LCD_HEIGHT / 10;
// 标注行编号
gfx->setTextColor(GREEN);
for (int x = 0; x < numRows; x++) {
gfx->setCursor(10 + x * 8, 2);
gfx->print(x, 16);
}
// 标注列编号
gfx->setTextColor(BLUE);
for (int y = 0; y < numCols; y++) {
gfx->setCursor(2, 12 + y * 10);
gfx->print(y, 16);
} -
绘制 ASCII 字符表 :
char c = 0;
for (int y = 0; y < numRows; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < numCols; x++) {
gfx->drawChar(10 + x * 8, 12 + y * 10, c++, WHITE, BLACK);
}
}
04_GFX_ESPWiFiAnalyzer
本示例演示了在 ST7789 显示器上绘制 WiFi 频段信号强度示例,实现 WiFi 分析器的功能。

代码
04_GFX_ESPWiFiAnalyzer.ino
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "Arduino_GFX_Library.h"
#include "pin_config.h"
#include <Wire.h>
#include "HWCDC.h"
HWCDC USBSerial;
Arduino_DataBus *bus = new Arduino_ESP32SPI(LCD_DC, LCD_CS, LCD_SCK, LCD_MOSI);
Arduino_GFX *gfx = new Arduino_ST7789(bus, LCD_RST /* RST */,
0 /* rotation */, true /* IPS */, LCD_WIDTH, LCD_HEIGHT, 0, 20, 0, 0);
#if defined(ESP32)
#include "WiFi.h"
#else
#include "ESP8266WiFi.h"
#define log_i(format, ...) Serial.printf(format, ##__VA_ARGS__)
#endif
int16_t w, h, text_size, banner_height, graph_baseline, graph_height, channel_width, signal_width;
// RSSI RANGE
#define RSSI_CEILING -40
#define RSSI_FLOOR -100
// Channel color mapping from channel 1 to 14
uint16_t channel_color[] = {
RED, ORANGE, YELLOW, GREEN, CYAN, BLUE, MAGENTA,
RED, ORANGE, YELLOW, GREEN, CYAN, BLUE, MAGENTA
};
uint8_t scan_count = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Serial.setDebugOutput(true);
// while(!Serial);
Serial.println("Arduino_GFX ESP WiFi Analyzer example");
// Set WiFi to station mode and disconnect from an AP if it was previously connected
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
WiFi.disconnect();
delay(100);
#ifdef GFX_EXTRA_PRE_INIT
GFX_EXTRA_PRE_INIT();
#endif
#if defined(LCD_PWR_PIN)
pinMode(LCD_PWR_PIN, OUTPUT); // sets the pin as output
digitalWrite(LCD_PWR_PIN, HIGH); // power on
#endif
// Init Display
if (!gfx->begin()) {
Serial.println("gfx->begin() failed!");
}
w = gfx->width();
h = gfx->height();
text_size = (h < 200) ? 1 : 2;
banner_height = text_size * 3 * 4;
graph_baseline = h - 20; // minus 2 text lines
graph_height = graph_baseline - banner_height - 30; // minus 3 text lines
channel_width = w / 17;
signal_width = channel_width * 2;
pinMode(LCD_BL, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LCD_BL, HIGH);
// init banner
gfx->setTextSize(text_size);
gfx->fillScreen(BLACK);
gfx->setTextColor(RED);
gfx->setCursor(0, 0);
gfx->print("ESP");
gfx->setTextColor(WHITE);
gfx->print(" WiFi Analyzer");
}
bool matchBssidPrefix(uint8_t *a, uint8_t *b) {
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 5; i++) { // only compare first 5 bytes
if (a[i] != b[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void loop() {
uint8_t ap_count_list[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 };
int32_t noise_list[] = { RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR };
int32_t peak_list[] = { RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_FLOOR };
int16_t peak_id_list[] = { -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1 };
int32_t channel;
int16_t idx;
int32_t rssi;
uint8_t *bssid;
String ssid;
uint16_t color;
int16_t height, offset, text_width;
// WiFi.scanNetworks will return the number of networks found
#if defined(ESP32)
int n = WiFi.scanNetworks(false /* async */, true /* show_hidden */, true /* passive */, 500 /* max_ms_per_chan */);
#else
int n = WiFi.scanNetworks(false /* async */, true /* show_hidden */);
#endif
// clear old graph
gfx->fillRect(0, banner_height, w, h - banner_height, BLACK);
gfx->setTextSize(1);
if (n == 0) {
gfx->setTextColor(WHITE);
gfx->setCursor(0, banner_height);
gfx->println("no networks found");
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
channel = WiFi.channel(i);
idx = channel - 1;
rssi = WiFi.RSSI(i);
bssid = WiFi.BSSID(i);
// channel peak stat
if (peak_list[idx] < rssi) {
peak_list[idx] = rssi;
peak_id_list[idx] = i;
}
// check signal come from same AP
bool duplicate_SSID = false;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if ((WiFi.channel(j) == channel) && matchBssidPrefix(WiFi.BSSID(j), bssid)) {
duplicate_SSID = true;
break;
}
}
if (!duplicate_SSID) {
ap_count_list[idx]++;
// noise stat
int32_t noise = rssi - RSSI_FLOOR;
noise *= noise;
if (channel > 4) {
noise_list[idx - 4] += noise;
}
if (channel > 3) {
noise_list[idx - 3] += noise;
}
if (channel > 2) {
noise_list[idx - 2] += noise;
}
if (channel > 1) {
noise_list[idx - 1] += noise;
}
noise_list[idx] += noise;
if (channel < 14) {
noise_list[idx + 1] += noise;
}
if (channel < 13) {
noise_list[idx + 2] += noise;
}
if (channel < 12) {
noise_list[idx + 3] += noise;
}
if (channel < 11) {
noise_list[idx + 4] += noise;
}
}
}
// plot found WiFi info
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
channel = WiFi.channel(i);
idx = channel - 1;
rssi = WiFi.RSSI(i);
color = channel_color[idx];
height = constrain(map(rssi, RSSI_FLOOR, RSSI_CEILING, 1, graph_height), 1, graph_height);
offset = (channel + 1) * channel_width;
// trim rssi with RSSI_FLOOR
if (rssi < RSSI_FLOOR) {
rssi = RSSI_FLOOR;
}
// plot chart
// gfx->drawLine(offset, graph_baseline - height, offset - signal_width, graph_baseline + 1, color);
// gfx->drawLine(offset, graph_baseline - height, offset + signal_width, graph_baseline + 1, color);
gfx->startWrite();
gfx->writeEllipseHelper(offset, graph_baseline + 1, signal_width, height, 0b0011, color);
gfx->endWrite();
if (i == peak_id_list[idx]) {
// Print SSID, signal strengh and if not encrypted
String ssid = WiFi.SSID(i);
if (ssid.length() == 0) {
ssid = WiFi.BSSIDstr(i);
}
text_width = (ssid.length() + 6) * 6;
if (text_width > w) {
offset = 0;
} else {
offset -= signal_width;
if ((offset + text_width) > w) {
offset = w - text_width;
}
}
gfx->setTextColor(color);
gfx->setCursor(offset, graph_baseline - 10 - height);
gfx->print(ssid);
gfx->print('(');
gfx->print(rssi);
gfx->print(')');
#if defined(ESP32)
if (WiFi.encryptionType(i) == WIFI_AUTH_OPEN)
#else
if (WiFi.encryptionType(i) == ENC_TYPE_NONE)
#endif
{
gfx->print('*');
}
}
}
}
// print WiFi stat
gfx->setTextColor(WHITE);
gfx->setCursor(0, banner_height);
gfx->print(n);
gfx->print(" networks found, lesser noise channels: ");
bool listed_first_channel = false;
int32_t min_noise = noise_list[0]; // init with channel 1 value
for (channel = 2; channel <= 11; channel++) // channels 12-14 may not available
{
idx = channel - 1;
log_i("min_noise: %d, noise_list[%d]: %d", min_noise, idx, noise_list[idx]);
if (noise_list[idx] < min_noise) {
min_noise = noise_list[idx];
}
}
for (channel = 1; channel <= 11; channel++) // channels 12-14 may not available
{
idx = channel - 1;
// check channel with min noise
if (noise_list[idx] == min_noise) {
if (!listed_first_channel) {
listed_first_channel = true;
} else {
gfx->print(", ");
}
gfx->print(channel);
}
}
// draw graph base axle
gfx->drawFastHLine(0, graph_baseline, gfx->width(), WHITE);
for (channel = 1; channel <= 14; channel++) {
idx = channel - 1;
offset = (channel + 1) * channel_width;
gfx->setTextColor(channel_color[idx]);
gfx->setCursor(offset - ((channel < 10) ? 3 : 6), graph_baseline + 2);
gfx->print(channel);
if (ap_count_list[idx] > 0) {
gfx->setCursor(offset - ((ap_count_list[idx] < 10) ? 9 : 12), graph_baseline + 8 + 2);
gfx->print('{');
gfx->print(ap_count_list[idx]);
gfx->print('}');
}
}
// Wait a bit before scanning again
// delay(SCAN_INTERVAL);
#if defined(SCAN_COUNT_SLEEP)
// POWER SAVING
if (++scan_count >= SCAN_COUNT_SLEEP) {
#if defined(LCD_PWR_PIN)
pinMode(LCD_PWR_PIN, INPUT); // disable pin
#endif
#if defined(GFX_BL)
pinMode(GFX_BL, INPUT); // disable pin
#endif
#if defined(ESP32)
esp_sleep_enable_ext0_wakeup(GPIO_NUM_36, LOW);
esp_deep_sleep_start();
#else
ESP.deepSleep(0);
#endif
}
#endif // defined(SCAN_COUNT_SLEEP)
}
代码解释
-
setup():初始化串口通信; 设置 WiFi 为站点模式并断开连接; 初始化显示屏,获取屏幕尺寸并计算各种绘图参数; 设置屏幕背景为黑色,绘制标题栏。
-
loop():扫描 WiFi 网络并获取网络信息,包括信道、RSSI、BSSID 和 SSID; 统计每个信道上的网络数量、噪声水平和峰值信号强度; 清除旧的图形并根据扫描结果绘制新的图形,包括信号强度椭圆和网络信息文本; 打印扫描到的网络数量和噪声最小的信道; 绘制图形基线和信道编号; 根据条件进入低功耗模式。
05_GFX_Clock
本示例演示了一个简单的 ST7789 时钟示例,通过简单的标记指针和时间管理实现时钟示例。

代码
05_GFX_Clock.ino
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "Arduino_GFX_Library.h"
#include "pin_config.h"
#include <Wire.h>
#include "HWCDC.h"
HWCDC USBSerial;
// SensorPCF85063 rtc;
Arduino_DataBus *bus = new Arduino_ESP32SPI(LCD_DC, LCD_CS, LCD_SCK, LCD_MOSI);
Arduino_GFX *gfx = new Arduino_ST7789(bus, LCD_RST /* RST */,
0 /* rotation */, true /* IPS */, LCD_WIDTH, LCD_HEIGHT, 0, 20, 0, 0);
#define BACKGROUND BLACK
#define MARK_COLOR WHITE
#define SUBMARK_COLOR DARKGREY // LIGHTGREY
#define HOUR_COLOR WHITE
#define MINUTE_COLOR BLUE // LIGHTGREY
#define SECOND_COLOR RED
#define SIXTIETH 0.016666667
#define TWELFTH 0.08333333
#define SIXTIETH_RADIAN 0.10471976
#define TWELFTH_RADIAN 0.52359878
#define RIGHT_ANGLE_RADIAN 1.5707963
static uint8_t conv2d(const char *p)
{
uint8_t v = 0;
return (10 * (*p - '0')) + (*++p - '0');
}
static int16_t w, h, center;
static int16_t hHandLen, mHandLen, sHandLen, markLen;
static float sdeg, mdeg, hdeg;
static int16_t osx = 0, osy = 0, omx = 0, omy = 0, ohx = 0, ohy = 0; // Saved H, M, S x & y coords
static int16_t nsx, nsy, nmx, nmy, nhx, nhy; // H, M, S x & y coords
static int16_t xMin, yMin, xMax, yMax; // redraw range
static int16_t hh, mm, ss;
static unsigned long targetTime; // next action time
static int16_t *cached_points;
static uint16_t cached_points_idx = 0;
static int16_t *last_cached_point;
void setup(void)
{
USBSerial.begin(115200);
USBSerial.println("Arduino_GFX Clock example");
// Init Display
if (!gfx->begin())
{
USBSerial.println("gfx->begin() failed!");
}
gfx->fillScreen(BACKGROUND);
pinMode(LCD_BL, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LCD_BL, HIGH);
// init LCD constant
w = gfx->width();
h = gfx->height();
if (w < h)
{
center = w / 2;
}
else
{
center = h / 2;
}
hHandLen = center * 3 / 8;
mHandLen = center * 2 / 3;
sHandLen = center * 5 / 6;
markLen = sHandLen / 6;
cached_points = (int16_t *)malloc((hHandLen + 1 + mHandLen + 1 + sHandLen + 1) * 2 * 2);
// Draw 60 clock marks
draw_round_clock_mark(
// draw_square_clock_mark(
center - markLen, center,
center - (markLen * 2 / 3), center,
center - (markLen / 2), center);
hh = conv2d(__TIME__);
mm = conv2d(__TIME__ + 3);
ss = conv2d(__TIME__ + 6);
targetTime = ((millis() / 1000) + 1) * 1000;
}
void loop()
{
unsigned long cur_millis = millis();
if (cur_millis >= targetTime)
{
targetTime += 1000;
ss++; // Advance second
if (ss == 60)
{
ss = 0;
mm++; // Advance minute
if (mm > 59)
{
mm = 0;
hh++; // Advance hour
if (hh > 23)
{
hh = 0;
}
}
}
}
// Pre-compute hand degrees, x & y coords for a fast screen update
sdeg = SIXTIETH_RADIAN * ((0.001 * (cur_millis % 1000)) + ss); // 0-59 (includes millis)
nsx = cos(sdeg - RIGHT_ANGLE_RADIAN) * sHandLen + center;
nsy = sin(sdeg - RIGHT_ANGLE_RADIAN) * sHandLen + center;
if ((nsx != osx) || (nsy != osy))
{
mdeg = (SIXTIETH * sdeg) + (SIXTIETH_RADIAN * mm); // 0-59 (includes seconds)
hdeg = (TWELFTH * mdeg) + (TWELFTH_RADIAN * hh); // 0-11 (includes minutes)
mdeg -= RIGHT_ANGLE_RADIAN;
hdeg -= RIGHT_ANGLE_RADIAN;
nmx = cos(mdeg) * mHandLen + center;
nmy = sin(mdeg) * mHandLen + center;
nhx = cos(hdeg) * hHandLen + center;
nhy = sin(hdeg) * hHandLen + center;
// redraw hands
redraw_hands_cached_draw_and_erase();
ohx = nhx;
ohy = nhy;
omx = nmx;
omy = nmy;
osx = nsx;
osy = nsy;
delay(1);
}
}
void draw_round_clock_mark(int16_t innerR1, int16_t outerR1, int16_t innerR2, int16_t outerR2, int16_t innerR3, int16_t outerR3)
{
float x, y;
int16_t x0, x1, y0, y1, innerR, outerR;
uint16_t c;
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 60; i++)
{
if ((i % 15) == 0)
{
innerR = innerR1;
outerR = outerR1;
c = MARK_COLOR;
}
else if ((i % 5) == 0)
{
innerR = innerR2;
outerR = outerR2;
c = MARK_COLOR;
}
else
{
innerR = innerR3;
outerR = outerR3;
c = SUBMARK_COLOR;
}
mdeg = (SIXTIETH_RADIAN * i) - RIGHT_ANGLE_RADIAN;
x = cos(mdeg);
y = sin(mdeg);
x0 = x * outerR + center;
y0 = y * outerR + center;
x1 = x * innerR + center;
y1 = y * innerR + center;
gfx->drawLine(x0, y0, x1, y1, c);
}
}
void draw_square_clock_mark(int16_t innerR1, int16_t outerR1, int16_t innerR2, int16_t outerR2, int16_t innerR3, int16_t outerR3)
{
float x, y;
int16_t x0, x1, y0, y1, innerR, outerR;
uint16_t c;
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 60; i++)
{
if ((i % 15) == 0)
{
innerR = innerR1;
outerR = outerR1;
c = MARK_COLOR;
}
else if ((i % 5) == 0)
{
innerR = innerR2;
outerR = outerR2;
c = MARK_COLOR;
}
else
{
innerR = innerR3;
outerR = outerR3;
c = SUBMARK_COLOR;
}
if ((i >= 53) || (i < 8))
{
x = tan(SIXTIETH_RADIAN * i);
x0 = center + (x * outerR);
y0 = center + (1 - outerR);
x1 = center + (x * innerR);
y1 = center + (1 - innerR);
}
else if (i < 23)
{
y = tan((SIXTIETH_RADIAN * i) - RIGHT_ANGLE_RADIAN);
x0 = center + (outerR);
y0 = center + (y * outerR);
x1 = center + (innerR);
y1 = center + (y * innerR);
}
else if (i < 38)
{
x = tan(SIXTIETH_RADIAN * i);
x0 = center - (x * outerR);
y0 = center + (outerR);
x1 = center - (x * innerR);
y1 = center + (innerR);
}
else if (i < 53)
{
y = tan((SIXTIETH_RADIAN * i) - RIGHT_ANGLE_RADIAN);
x0 = center + (1 - outerR);
y0 = center - (y * outerR);
x1 = center + (1 - innerR);
y1 = center - (y * innerR);
}
gfx->drawLine(x0, y0, x1, y1, c);
}
}
void redraw_hands_cached_draw_and_erase()
{
gfx->startWrite();
draw_and_erase_cached_line(center, center, nsx, nsy, SECOND_COLOR, cached_points, sHandLen + 1, false, false);
draw_and_erase_cached_line(center, center, nhx, nhy, HOUR_COLOR, cached_points + ((sHandLen + 1) * 2), hHandLen + 1, true, false);
draw_and_erase_cached_line(center, center, nmx, nmy, MINUTE_COLOR, cached_points + ((sHandLen + 1 + hHandLen + 1) * 2), mHandLen + 1, true, true);
gfx->endWrite();
}
void draw_and_erase_cached_line(int16_t x0, int16_t y0, int16_t x1, int16_t y1, int16_t color, int16_t *cache, int16_t cache_len, bool cross_check_second, bool cross_check_hour)
{
#if defined(ESP8266)
yield();
#endif
bool steep = _diff(y1, y0) > _diff(x1, x0);
if (steep)
{
_swap_int16_t(x0, y0);
_swap_int16_t(x1, y1);
}
int16_t dx, dy;
dx = _diff(x1, x0);
dy = _diff(y1, y0);
int16_t err = dx / 2;
int8_t xstep = (x0 < x1) ? 1 : -1;
int8_t ystep = (y0 < y1) ? 1 : -1;
x1 += xstep;
int16_t x, y, ox, oy;
for (uint16_t i = 0; i <= dx; i++)
{
if (steep)
{
x = y0;
y = x0;
}
else
{
x = x0;
y = y0;
}
ox = *(cache + (i * 2));
oy = *(cache + (i * 2) + 1);
if ((x == ox) && (y == oy))
{
if (cross_check_second || cross_check_hour)
{
write_cache_pixel(x, y, color, cross_check_second, cross_check_hour);
}
}
else
{
write_cache_pixel(x, y, color, cross_check_second, cross_check_hour);
if ((ox > 0) || (oy > 0))
{
write_cache_pixel(ox, oy, BACKGROUND, cross_check_second, cross_check_hour);
}
*(cache + (i * 2)) = x;
*(cache + (i * 2) + 1) = y;
}
if (err < dy)
{
y0 += ystep;
err += dx;
}
err -= dy;
x0 += xstep;
}
for (uint16_t i = dx + 1; i < cache_len; i++)
{
ox = *(cache + (i * 2));
oy = *(cache + (i * 2) + 1);
if ((ox > 0) || (oy > 0))
{
write_cache_pixel(ox, oy, BACKGROUND, cross_check_second, cross_check_hour);
}
*(cache + (i * 2)) = 0;
*(cache + (i * 2) + 1) = 0;
}
}
void write_cache_pixel(int16_t x, int16_t y, int16_t color, bool cross_check_second, bool cross_check_hour)
{
int16_t *cache = cached_points;
if (cross_check_second)
{
for (uint16_t i = 0; i <= sHandLen; i++)
{
if ((x == *(cache++)) && (y == *(cache)))
{
return;
}
cache++;
}
}
if (cross_check_hour)
{
cache = cached_points + ((sHandLen + 1) * 2);
for (uint16_t i = 0; i <= hHandLen; i++)
{
if ((x == *(cache++)) && (y == *(cache)))
{
return;
}
cache++;
}
}
gfx->writePixel(x, y, color);
}
代码解释
-
时针、分针、秒针的绘制 :
void redraw_hands_cached_draw_and_erase() {
gfx->startWrite();
draw_and_erase_cached_line(center, center, nsx, nsy, SECOND_COLOR, cached_points, sHandLen + 1, false, false);
draw_and_erase_cached_line(center, center, nhx, nhy, HOUR_COLOR, cached_points + ((sHandLen + 1) * 2), hHandLen + 1, true, false);
draw_and_erase_cached_line(center, center, nmx, nmy, MINUTE_COLOR, cached_points + ((sHandLen + 1 + hHandLen + 1) * 2), mHandLen + 1, true, true);
gfx->endWrite();
}
06_GFX_PCF85063_simpleTime
本示例演示了使用 PCF85063 RTC 模块在 ST7789 显示屏上显示当前时间,每秒检索时间并仅在时间发生变化时更新显示。

代码
06_GFX_PCF85063_simpleTime.ino
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "Arduino_GFX_Library.h"
#include "pin_config.h"
#include "SensorPCF85063.hpp"
#include <Wire.h>
#include "HWCDC.h"
HWCDC USBSerial;
SensorPCF85063 rtc;
uint32_t lastMillis;
char previousTimeString[20] = "";
Arduino_DataBus *bus = new Arduino_ESP32SPI(LCD_DC, LCD_CS, LCD_SCK, LCD_MOSI);
Arduino_GFX *gfx = new Arduino_ST7789(bus, LCD_RST /* RST */,
0 /* rotation */, true /* IPS */, LCD_WIDTH, LCD_HEIGHT, 0, 20, 0, 0);
int16_t getCenteredX(const char *text, uint8_t textSize) {
int16_t textWidth = strlen(text) * 3 * textSize; // 6 pixels per character in default size
return (LCD_WIDTH - textWidth) / 2;
}
void setup() {
USBSerial.begin(115200);
if (!rtc.begin(Wire, PCF85063_SLAVE_ADDRESS, IIC_SDA, IIC_SCL)) {
USBSerial.println("Failed to find PCF8563 - check your wiring!");
while (1) {
delay(1000);
}
}
uint16_t year = 2024;
uint8_t month = 9;
uint8_t day = 24;
uint8_t hour = 11;
uint8_t minute = 24;
uint8_t second = 30;
rtc.setDateTime(year, month, day, hour, minute, second);
gfx->begin();
gfx->fillScreen(WHITE);
pinMode(LCD_BL, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LCD_BL, HIGH);
}
void loop() {
if (millis() - lastMillis > 1000) {
lastMillis = millis();
RTC_DateTime datetime = rtc.getDateTime();
// Format the current time as a string
char timeString[20];
sprintf(timeString, "%04d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d",
datetime.year, datetime.month, datetime.day,
datetime.hour, datetime.minute, datetime.second);
// Only update the time if it has changed
if (strcmp(timeString, previousTimeString) != 0) {
// Clear the previous time area by filling a small rectangle
gfx->fillRect(0, 150, LCD_WIDTH, 50, WHITE); // Clear the area for the time
gfx->setTextColor(BLACK);
gfx->setTextSize(3,3,0);
int16_t timeX = getCenteredX(timeString, 3);
gfx->setCursor(timeX, 150); // Adjust Y-coordinate as needed
gfx->println(timeString); // Display the new time
// Save the current time as the previous time
strcpy(previousTimeString, timeString);
}
}
}
代码解释
loop():- 首先获取当前时间,如果当前时间与上一次显示的时间不同,则进行以下操作:
- 清除上一次显示时间的区域,通过填充一个矩形实现,以便更新时间显示时不会出现重叠。
- 设置文本颜色为黑色,并设置文本大小为 3。
- 调用
getCenteredX函数计算当前时间字符串在屏幕上居中显示的 X 坐标。 - 设置光标位置并打印当前时间字符串,实现时间的更新显示。
- 将当前时间字符串复制到
previousTimeString,以便下次判断时间是否变化。
07_LVGL_Measuring_voltage
本示例展示如何使用 LVGL 库和 Arduino GFX 库,实现显示屏文本更新和电压测量。代码初始化了 ST7789 显示屏,在显示屏中心创建一个标签,并周期性地读取电压分压器的实际电压值,更新标签以显示最新的电压信息。

代码
07_LVGL_Measuring_voltage.ino
#include <lvgl.h>
#include "Arduino_GFX_Library.h"
#include "lv_conf.h"
#include "demos/lv_demos.h"
#include "pin_config.h"
/* Using LVGL with Arduino requires some extra steps:
* Be sure to read the docs here: https://docs.lvgl.io/master/get-started/platforms/arduino.html */
#define EXAMPLE_LVGL_TICK_PERIOD_MS 2
/* Change to your screen resolution */
static const uint16_t screenWidth = 240;
static const uint16_t screenHeight = 280;
static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf;
static lv_color_t buf[screenWidth * screenHeight / 10];
const int voltageDividerPin = 1; // GPIO1 pin
float vRef = 3.3; // Power supply voltage of ESP32-S3 (unit: volts)
float R1 = 200000.0; // Resistance value of the first resistor (unit: ohms)
float R2 = 100000.0; // Resistance value of the second resistor (unit: ohms)
lv_obj_t *label; // Global label object
Arduino_DataBus *bus = new Arduino_ESP32SPI(LCD_DC, LCD_CS, LCD_SCK, LCD_MOSI);
Arduino_GFX *gfx = new Arduino_ST7789(bus, LCD_RST /* RST */,
0 /* rotation */, true /* IPS */, LCD_WIDTH, LCD_HEIGHT, 0, 20, 0, 0);
#if LV_USE_LOG!= 0
/* Serial debugging */
void my_print(const char *buf) {
Serial.printf(buf);
Serial.flush();
}
#endif
/* Display flushing */
void my_disp_flush(lv_disp_drv_t *disp, const lv_area_t *area, lv_color_t *color_p) {
uint32_t w = (area->x2 - area->x1 + 1);
uint32_t h = (area->y2 - area->y1 + 1);
#if (LV_COLOR_16_SWAP!= 0)
gfx->draw16bitBeRGBBitmap(area->x1, area->y1, (uint16_t *)&color_p->full, w, h);
#else
gfx->draw16bitRGBBitmap(area->x1, area->y1, (uint16_t *)&color_p->full, w, h);
#endif
lv_disp_flush_ready(disp);
}
void example_increase_lvgl_tick(void *arg) {
/* Tell LVGL how many milliseconds has elapsed */
lv_tick_inc(EXAMPLE_LVGL_TICK_PERIOD_MS);
}
static uint8_t count = 0;
void example_increase_reboot(void *arg) {
count++;
if (count == 30) {
esp_restart();
}
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); /* prepare for possible serial debug */
pinMode(voltageDividerPin, INPUT);
String LVGL_Arduino = "Hello Arduino! ";
LVGL_Arduino += String('V') + lv_version_major() + "." + lv_version_minor() + "." + lv_version_patch();
Serial.println(LVGL_Arduino);
Serial.println("I am LVGL_Arduino");
lv_init();
#if LV_USE_LOG!= 0
lv_log_register_print_cb(my_print); /* register print function for debugging */
#endif
gfx->begin();
pinMode(LCD_BL, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LCD_BL, HIGH);
lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf, buf, NULL, screenWidth * screenHeight / 10);
/* Initialize the display */
static lv_disp_drv_t disp_drv;
lv_disp_drv_init(&disp_drv);
/* Change the following line to your display resolution */
disp_drv.hor_res = screenWidth;
disp_drv.ver_res = screenHeight;
disp_drv.flush_cb = my_disp_flush;
disp_drv.draw_buf = &draw_buf;
lv_disp_drv_register(&disp_drv);
const esp_timer_create_args_t lvgl_tick_timer_args = {
.callback = &example_increase_lvgl_tick,
.name = "lvgl_tick"
};
const esp_timer_create_args_t reboot_timer_args = {
.callback = &example_increase_reboot,
.name = "reboot"
};
esp_timer_handle_t lvgl_tick_timer = NULL;
esp_timer_create(&lvgl_tick_timer_args, &lvgl_tick_timer);
esp_timer_start_periodic(lvgl_tick_timer, EXAMPLE_LVGL_TICK_PERIOD_MS * 1000);
// esp_timer_handle_t reboot_timer = NULL;
// esp_timer_create(&reboot_timer_args, &reboot_timer);
// esp_timer_start_periodic(reboot_timer, 2000 * 1000);
/* Create label */
label = lv_label_create(lv_scr_act());
lv_label_set_text(label, "Initializing...");
lv_obj_align(label, LV_ALIGN_CENTER, 0, 0);
Serial.println("Setup done");
}
void loop() {
lv_timer_handler(); /* let the GUI do its work */
delay(5);
// Read ADC value
int adcValue = analogRead(voltageDividerPin);
// Convert to voltage
float voltage = (float)adcValue * (vRef / 4095.0);
// Apply the voltage divider formula to calculate the actual voltage
float actualVoltage = voltage * ((R1 + R2) / R2);
// Print the actual voltage
Serial.print("Actual Voltage: ");
Serial.print(actualVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
// Update label content
String voltageStr = "Actual Voltage: " + String(actualVoltage) + " V";
lv_label_set_text(label, voltageStr.c_str());
}
代码解释
my_print():用于 LVGL 的日志输出,如果启用了 LVGL 的日志功能,这个函数会将日志信息打印到串口my_disp_flush():负责将 LVGL 的绘图缓冲区内容刷新到显示屏上example_increase_lvgl_tick():定时器回调函数,用于通知 LVGL 时间的流逝example_increase_reboot():另一个定时器回调函数,用于计数,达到一定次数后可能触发系统重启
08_LVGL_PCF85063_simpleTime
本示例演示了在 LVGL 下使用 PCF85063 RTC 模块在 ST7789 显示屏上显示当前时间,每秒检索时间并仅在时间发生变化时更新显示。

代码
08_LVGL_PCF85063_simpleTime.ino
#include <lvgl.h>
#include "Arduino_GFX_Library.h"
#include "pin_config.h"
#include "lv_conf.h"
#include <Wire.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Arduino.h>
#include "SensorPCF85063.hpp"
#include "HWCDC.h"
HWCDC USBSerial;
#define EXAMPLE_LVGL_TICK_PERIOD_MS 2
static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf;
static lv_color_t buf[LCD_WIDTH * LCD_HEIGHT / 10];
lv_obj_t *label; // Global label object
SensorPCF85063 rtc;
uint32_t lastMillis;
Arduino_DataBus *bus = new Arduino_ESP32SPI(LCD_DC, LCD_CS, LCD_SCK, LCD_MOSI);
Arduino_GFX *gfx = new Arduino_ST7789(bus, LCD_RST /* RST */,
0 /* rotation */, true /* IPS */, LCD_WIDTH, LCD_HEIGHT, 0, 20, 0, 0);
#if LV_USE_LOG != 0
/* Serial debugging */
void my_print(const char *buf) {
USBSerial.printf(buf);
USBSerial.flush();
}
#endif
/* Display flushing */
void my_disp_flush(lv_disp_drv_t *disp, const lv_area_t *area, lv_color_t *color_p) {
uint32_t w = (area->x2 - area->x1 + 1);
uint32_t h = (area->y2 - area->y1 + 1);
#if (LV_COLOR_16_SWAP != 0)
gfx->draw16bitBeRGBBitmap(area->x1, area->y1, (uint16_t *)&color_p->full, w, h);
#else
gfx->draw16bitRGBBitmap(area->x1, area->y1, (uint16_t *)&color_p->full, w, h);
#endif
lv_disp_flush_ready(disp);
}
void example_increase_lvgl_tick(void *arg) {
/* Tell LVGL how many milliseconds has elapsed */
lv_tick_inc(EXAMPLE_LVGL_TICK_PERIOD_MS);
}
static uint8_t count = 0;
void example_increase_reboot(void *arg) {
count++;
if (count == 30) {
esp_restart();
}
}
void setup() {
USBSerial.begin(115200); /* prepare for possible serial debug */
if (!rtc.begin(Wire, PCF85063_SLAVE_ADDRESS, IIC_SDA, IIC_SCL)) {
USBSerial.println("Failed to find PCF8563 - check your wiring!");
while (1) {
delay(1000);
}
}
uint16_t year = 2024;
uint8_t month = 9;
uint8_t day = 24;
uint8_t hour = 11;
uint8_t minute = 9;
uint8_t second = 41;
rtc.setDateTime(year, month, day, hour, minute, second);
gfx->begin();
pinMode(LCD_BL, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LCD_BL, HIGH);
String LVGL_Arduino = "Hello Arduino! ";
LVGL_Arduino += String('V') + lv_version_major() + "." + lv_version_minor() + "." + lv_version_patch();
USBSerial.println(LVGL_Arduino);
USBSerial.println("I am LVGL_Arduino");
lv_init();
#if LV_USE_LOG != 0
lv_log_register_print_cb(my_print); /* register print function for debugging */
#endif
lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf, buf, NULL, LCD_WIDTH * LCD_HEIGHT / 10);
/*Initialize the display*/
static lv_disp_drv_t disp_drv;
lv_disp_drv_init(&disp_drv);
/*Change the following line to your display resolution*/
disp_drv.hor_res = LCD_WIDTH;
disp_drv.ver_res = LCD_HEIGHT;
disp_drv.flush_cb = my_disp_flush;
disp_drv.draw_buf = &draw_buf;
lv_disp_drv_register(&disp_drv);
/*Initialize the (dummy) input device driver*/
static lv_indev_drv_t indev_drv;
lv_indev_drv_init(&indev_drv);
indev_drv.type = LV_INDEV_TYPE_POINTER;
lv_indev_drv_register(&indev_drv);
// lv_obj_t *label = lv_label_create(lv_scr_act());
// lv_label_set_text(label, "Hello Ardino and LVGL!");
// lv_obj_align(label, LV_ALIGN_CENTER, 0, 0);
const esp_timer_create_args_t lvgl_tick_timer_args = {
.callback = &example_increase_lvgl_tick,
.name = "lvgl_tick"
};
const esp_timer_create_args_t reboot_timer_args = {
.callback = &example_increase_reboot,
.name = "reboot"
};
esp_timer_handle_t lvgl_tick_timer = NULL;
esp_timer_create(&lvgl_tick_timer_args, &lvgl_tick_timer);
esp_timer_start_periodic(lvgl_tick_timer, EXAMPLE_LVGL_TICK_PERIOD_MS * 1000);
label = lv_label_create(lv_scr_act());
lv_label_set_text(label, "Initializing...");
lv_obj_align(label, LV_ALIGN_CENTER, 0, 0);
}
void loop() {
lv_timer_handler(); /* let the GUI do its work */
delay(5);
if (millis() - lastMillis > 1000) {
lastMillis = millis();
RTC_DateTime datetime = rtc.getDateTime();
USBSerial.printf(" Year :");
USBSerial.print(datetime.year);
USBSerial.printf(" Month:");
USBSerial.print(datetime.month);
USBSerial.printf(" Day :");
USBSerial.print(datetime.day);
USBSerial.printf(" Hour:");
USBSerial.print(datetime.hour);
USBSerial.printf(" Minute:");
USBSerial.print(datetime.minute);
USBSerial.printf(" Sec :");
USBSerial.println(datetime.second);
char buf[32];
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%02d:%02d:%02d\n%02d-%02d-%04d",
datetime.hour, datetime.minute, datetime.second,
datetime.day, datetime.month, datetime.year);
// Update label with current time
lv_label_set_text(label, buf);
lv_obj_set_style_text_font(label, &lv_font_montserrat_40, LV_PART_MAIN);
}
delay(20);
}
代码解释
-
setup():- 初始化串口通信,以 115200 的波特率准备可能的串口调试;
- 尝试连接 PCF85063 实时时钟芯片,如果连接失败则进入死循环;
- 设置实时时钟的初始时间为 2024 年 9 月 24 日 11 时 9 分 41 秒;
- 初始化显示屏,设置屏幕亮度;
- 初始化 LVGL,并注册日志输出函数(如果启用了日志功能;
- 配置 LVGL 的显示驱动和绘图缓冲区,以及初始化输入设备驱动(虽然是一个虚拟的指针输入设备驱动)
- 创建定时器用于定期触发 LVGL 的时钟更新
- 创建一个标签并设置初始文本为 “Initializing...”
-
loop():- 调用
lv_timer_handler让 LVGL 处理图形界面的任务; - 每秒钟检查一次时间是否更新,如果是,则获取实时时钟的当前时间,通过串口输出,并将时间格式化为特定格式后更新标签的文本内容,同时设置标签的字体为
lv_font_montserrat_40。
- 调用
09_LVGL_Keys_Bee
本示例展示了如何使用 LVGL 库结合 Arduino 和 ESP32 来实现一个带有简单 GUI 交互的按键响应系统。该代码允许用户通过按键检测单击、双击和长按事件,并将相应的输出显示在连接的液晶屏幕上。
具体功能实现包括:利用触发操作在屏幕上显示 "Single Click"、"Double Click" 和 "Long Press" 字样,并在长按时启用蜂鸣器。程序通过 LVGL 的绘图功能实现屏幕刷新,并通过简单的去抖动机制提高按键识别的准确性。此外,还设置了自动重启机制用于长时间运行的设备维护。

代码
09_LVGL_Keys_Bee.ino
#error "按键失灵时,请修改 USE_NEW_PIN_CONFIG 为 1 以使用新的引脚配置。运行代码时,请注释此行,If the key fails, change USE_NEW_PIN_CONFIG to 1 to use the new pin configuration. Comment this line as you run the code"
#include <lvgl.h>
#include "Arduino_GFX_Library.h"
#include "lv_conf.h"
#include "demos/lv_demos.h"
#include "pin_config.h"
#include <Wire.h>
#include "HWCDC.h"
HWCDC USBSerial;
/*To use the built-in examples and demos of LVGL uncomment the includes below respectively.
*You also need to copy `lvgl/examples` to `lvgl/src/examples`. Similarly for the demos `lvgl/demos` to `lvgl/src/demos`.
Note that the `lv_examples` library is for LVGL v7 and you shouldn't install it for this version (since LVGL v8)
as the examples and demos are now part of the main LVGL library. */
#define EXAMPLE_LVGL_TICK_PERIOD_MS 2
#define USE_NEW_PIN_CONFIG 0
#if (USE_NEW_PIN_CONFIG)
// New pin configuration
const int inputPin = 40; // Define GPIO40 as input
const int outputPin = 41; // Define GPIO41 as output
const int beePin = 42; // Define GPIO42 for buzzer
#else
// Existing pin configuration
const int inputPin = 36; // Define GPIO36 as input
const int outputPin = 35; // Define GPIO35 as output
const int beePin = 33; // Define GPIO33 for buzzer
#endif
bool buttonState = false;
bool lastButtonState = false;
unsigned long lastDebounceTime = 0;
unsigned long debounceDelay = 50;
unsigned long lastClickTime = 0;
unsigned long clickInterval = 500; // Double-click interval
unsigned long longPressDuration = 1000; // Long press duration
bool longPressDetected = false;
bool doubleClickDetected = false;
bool clickDetected = false;
/*Change to your screen resolution*/
static const uint16_t screenWidth = 240;
static const uint16_t screenHeight = 280;
static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf;
static lv_color_t buf[screenWidth * screenHeight / 10];
lv_obj_t *label; // Global label object
Arduino_DataBus *bus = new Arduino_ESP32SPI(LCD_DC, LCD_CS, LCD_SCK, LCD_MOSI);
Arduino_GFX *gfx = new Arduino_ST7789(bus, LCD_RST /* RST */,
0 /* rotation */, true /* IPS */, LCD_WIDTH, LCD_HEIGHT, 0, 20, 0, 0);
#if LV_USE_LOG != 0
/* USBSerial debugging */
void my_print(const char *buf) {
USBSerial.printf(buf);
USBSerial.flush();
}
#endif
/* Display flushing */
void my_disp_flush(lv_disp_drv_t *disp, const lv_area_t *area, lv_color_t *color_p) {
uint32_t w = (area->x2 - area->x1 + 1);
uint32_t h = (area->y2 - area->y1 + 1);
#if (LV_COLOR_16_SWAP != 0)
gfx->draw16bitBeRGBBitmap(area->x1, area->y1, (uint16_t *)&color_p->full, w, h);
#else
gfx->draw16bitRGBBitmap(area->x1, area->y1, (uint16_t *)&color_p->full, w, h);
#endif
lv_disp_flush_ready(disp);
}
void example_increase_lvgl_tick(void *arg) {
/* Tell LVGL how many milliseconds has elapsed */
lv_tick_inc(EXAMPLE_LVGL_TICK_PERIOD_MS);
}
static uint8_t count = 0;
void example_increase_reboot(void *arg) {
count++;
if (count == 30) {
esp_restart();
}
}
void setup() {
pinMode(inputPin, INPUT);
pinMode(outputPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(beePin, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(outputPin, HIGH); // Initialize output pin to HIGH
gfx->begin();
pinMode(LCD_BL, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LCD_BL, HIGH);
String LVGL_Arduino = "Hello Arduino! ";
LVGL_Arduino += String('V') + lv_version_major() + "." + lv_version_minor() + "." + lv_version_patch();
USBSerial.println(LVGL_Arduino);
USBSerial.println("I am LVGL_Arduino");
lv_init();
#if LV_USE_LOG != 0
lv_log_register_print_cb(my_print); /* register print function for debugging */
#endif
lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf, buf, NULL, screenWidth * screenHeight / 10);
/*Initialize the display*/
static lv_disp_drv_t disp_drv;
lv_disp_drv_init(&disp_drv);
/*Change the following line to your display resolution*/
disp_drv.hor_res = screenWidth;
disp_drv.ver_res = screenHeight;
disp_drv.flush_cb = my_disp_flush;
disp_drv.draw_buf = &draw_buf;
lv_disp_drv_register(&disp_drv);
const esp_timer_create_args_t lvgl_tick_timer_args = {
.callback = &example_increase_lvgl_tick,
.name = "lvgl_tick"
};
const esp_timer_create_args_t reboot_timer_args = {
.callback = &example_increase_reboot,
.name = "reboot"
};
esp_timer_handle_t lvgl_tick_timer = NULL;
esp_timer_create(&lvgl_tick_timer_args, &lvgl_tick_timer);
esp_timer_start_periodic(lvgl_tick_timer, EXAMPLE_LVGL_TICK_PERIOD_MS * 1000);
// esp_timer_handle_t reboot_timer = NULL;
// esp_timer_create(&reboot_timer_args, &reboot_timer);
// esp_timer_start_periodic(reboot_timer, 2000 * 1000);
label = lv_label_create(lv_scr_act());
lv_label_set_text(label, "Initializing...");
lv_obj_align(label, LV_ALIGN_CENTER, 0, 0);
USBSerial.println("Setup done");
}
void loop() {
lv_timer_handler(); /* let the GUI do its work */
delay(5);
int reading = digitalRead(inputPin);
// Debounce processing
if (reading != lastButtonState) {
lastDebounceTime = millis();
}
if ((millis() - lastDebounceTime) > debounceDelay) {
if (reading != buttonState) {
buttonState = reading;
if (buttonState == LOW) {
// Operation when button is pressed
unsigned long now = millis();
if (now - lastClickTime < clickInterval && !longPressDetected) {
lv_label_set_text(label, "Double Click");
// Double click detected
printf("Double Click\n");
doubleClickDetected = true;
} else {
// Single click detected
if (!longPressDetected && !doubleClickDetected) {
lv_label_set_text(label, "Single Click");
printf("Single Click\n");
clickDetected = true;
}
}
lastClickTime = now;
delay(100); // Used to eliminate button noise
} else {
// Operation when button is released
if (longPressDetected) {
lv_label_set_text(label, "Long Press Released");
// Set GPIO35 output to low level after long pressing the button and releasing it
printf("Long Press Released\n");
noTone(beePin);
digitalWrite(outputPin, LOW); // Set GPIO35 output to low level
longPressDetected = false; // Reset long press detection flag
}
clickDetected = false;
doubleClickDetected = false;
}
}
}
// Check if the button is in long press state
if (buttonState == LOW && (millis() - lastDebounceTime >= longPressDuration)) {
lv_label_set_text(label, "Long Press");
// Long press button
printf("Long Press\n");
tone(beePin, 2000);
longPressDetected = true; // Set long press detection flag
clickDetected = false; // Reset single click detection flag
doubleClickDetected = false; // Reset double click detection flag
}
lastButtonState = reading;
}
代码解释
loop():- 调用
lv_timer_handler让 LVGL 处理图形界面的任务; - 读取输入引脚的状态,进行去抖动处理;
- 根据按钮的状态(按下或释放)以及时间间隔判断是单点击、双点击还是长按事件,并更新显示屏上的标签文本以显示相应的事件信息;
- 同时,对于长按事件会触发蜂鸣器发声,释放时则停止蜂鸣器并将特定输出引脚设置为低电平。
- 调用
10_LVGL_QMI8658_ui
本示例演示了使用 LVGL 进行图形显示,与 QMI8658 IMU 通信以获取加速度计和陀螺仪数据。

代码
10_LVGL_QMI8658_ui.ino
#include <lvgl.h>
#include "Arduino_GFX_Library.h"
#include "pin_config.h"
#include "lv_conf.h"
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include "SensorQMI8658.hpp"
#include "HWCDC.h"
HWCDC USBSerial;
#define EXAMPLE_LVGL_TICK_PERIOD_MS 2
static lv_disp_draw_buf_t draw_buf;
static lv_color_t buf[LCD_WIDTH * LCD_HEIGHT / 10];
SensorQMI8658 qmi;
IMUdata acc;
IMUdata gyr;
lv_obj_t *label; // Global label object
lv_obj_t *chart; // Global chart object
lv_chart_series_t *acc_series_x; // Acceleration X series
lv_chart_series_t *acc_series_y; // Acceleration Y series
lv_chart_series_t *acc_series_z; // Acceleration Z series
Arduino_DataBus *bus = new Arduino_ESP32SPI(LCD_DC, LCD_CS, LCD_SCK, LCD_MOSI);
Arduino_GFX *gfx = new Arduino_ST7789(bus, LCD_RST /* RST */,
0 /* rotation */, true /* IPS */, LCD_WIDTH, LCD_HEIGHT, 0, 20, 0, 0);
#if LV_USE_LOG != 0
/* Serial debugging */
void my_print(const char *buf) {
USBSerial.printf(buf);
USBSerial.flush();
}
#endif
/* Display flushing */
void my_disp_flush(lv_disp_drv_t *disp, const lv_area_t *area, lv_color_t *color_p) {
uint32_t w = (area->x2 - area->x1 + 1);
uint32_t h = (area->y2 - area->y1 + 1);
#if (LV_COLOR_16_SWAP != 0)
gfx->draw16bitBeRGBBitmap(area->x1, area->y1, (uint16_t *)&color_p->full, w, h);
#else
gfx->draw16bitRGBBitmap(area->x1, area->y1, (uint16_t *)&color_p->full, w, h);
#endif
lv_disp_flush_ready(disp);
}
void example_increase_lvgl_tick(void *arg) {
/* Tell LVGL how many milliseconds has elapsed */
lv_tick_inc(EXAMPLE_LVGL_TICK_PERIOD_MS);
}
static uint8_t count = 0;
void example_increase_reboot(void *arg) {
count++;
if (count == 30) {
esp_restart();
}
}
void setup() {
USBSerial.begin(115200); /* prepare for possible serial debug */
// pinMode(LCD_EN, OUTPUT);
// digitalWrite(LCD_EN, HIGH);
gfx->begin();
pinMode(LCD_BL, OUTPUT);
pinMode(38, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LCD_BL, HIGH);
digitalWrite(38, HIGH);
String LVGL_Arduino = "Hello Arduino! ";
LVGL_Arduino += String('V') + lv_version_major() + "." + lv_version_minor() + "." + lv_version_patch();
USBSerial.println(LVGL_Arduino);
USBSerial.println("I am LVGL_Arduino");
lv_init();
#if LV_USE_LOG != 0
lv_log_register_print_cb(my_print); /* register print function for debugging */
#endif
lv_disp_draw_buf_init(&draw_buf, buf, NULL, LCD_WIDTH * LCD_HEIGHT / 10);
/*Initialize the display*/
static lv_disp_drv_t disp_drv;
lv_disp_drv_init(&disp_drv);
/*Change the following line to your display resolution*/
disp_drv.hor_res = LCD_WIDTH;
disp_drv.ver_res = LCD_HEIGHT;
disp_drv.flush_cb = my_disp_flush;
disp_drv.draw_buf = &draw_buf;
lv_disp_drv_register(&disp_drv);
/*Initialize the (dummy) input device driver*/
static lv_indev_drv_t indev_drv;
lv_indev_drv_init(&indev_drv);
indev_drv.type = LV_INDEV_TYPE_POINTER;
lv_indev_drv_register(&indev_drv);
lv_obj_t *label = lv_label_create(lv_scr_act());
lv_label_set_text(label, "Hello Ardino and LVGL!");
lv_obj_align(label, LV_ALIGN_CENTER, 0, 0);
const esp_timer_create_args_t lvgl_tick_timer_args = {
.callback = &example_increase_lvgl_tick,
.name = "lvgl_tick"
};
const esp_timer_create_args_t reboot_timer_args = {
.callback = &example_increase_reboot,
.name = "reboot"
};
esp_timer_handle_t lvgl_tick_timer = NULL;
esp_timer_create(&lvgl_tick_timer_args, &lvgl_tick_timer);
esp_timer_start_periodic(lvgl_tick_timer, EXAMPLE_LVGL_TICK_PERIOD_MS * 1000);
label = lv_label_create(lv_scr_act());
lv_label_set_text(label, "Initializing...");
lv_obj_align(label, LV_ALIGN_CENTER, 0, 0);
/* Create chart */
chart = lv_chart_create(lv_scr_act());
lv_obj_set_size(chart, 240, 280);
lv_obj_align(chart, LV_ALIGN_CENTER, 0, 0);
lv_chart_set_type(chart, LV_CHART_TYPE_LINE); /* Set the type to line */
lv_chart_set_range(chart, LV_CHART_AXIS_PRIMARY_Y, -3, 3); /* Set the range of y axis */
lv_chart_set_point_count(chart, 20); /* Set the number of data points */
acc_series_x = lv_chart_add_series(chart, lv_palette_main(LV_PALETTE_RED), LV_CHART_AXIS_PRIMARY_Y);
acc_series_y = lv_chart_add_series(chart, lv_palette_main(LV_PALETTE_GREEN), LV_CHART_AXIS_PRIMARY_Y);
acc_series_z = lv_chart_add_series(chart, lv_palette_main(LV_PALETTE_BLUE), LV_CHART_AXIS_PRIMARY_Y);
USBSerial.println("Setup done");
if (!qmi.begin(Wire, QMI8658_L_SLAVE_ADDRESS, IIC_SDA, IIC_SCL)) {
while (1) {
delay(1000);
}
}
/* Get chip id */
USBSerial.println(qmi.getChipID());
qmi.configAccelerometer(
SensorQMI8658::ACC_RANGE_4G,
SensorQMI8658::ACC_ODR_1000Hz,
SensorQMI8658::LPF_MODE_0,
true);
qmi.configGyroscope(
SensorQMI8658::GYR_RANGE_64DPS,
SensorQMI8658::GYR_ODR_896_8Hz,
SensorQMI8658::LPF_MODE_3,
true);
qmi.enableGyroscope();
qmi.enableAccelerometer();
qmi.dumpCtrlRegister();
USBSerial.println("Read data now...");
}
void loop() {
lv_timer_handler(); /* let the GUI do its work */
delay(5);
if (qmi.getDataReady()) {
if (qmi.getAccelerometer(acc.x, acc.y, acc.z)) {
USBSerial.print("{ACCEL: ");
USBSerial.print(acc.x);
USBSerial.print(",");
USBSerial.print(acc.y);
USBSerial.print(",");
USBSerial.print(acc.z);
USBSerial.println("}");
// Update chart with new accelerometer data
lv_chart_set_next_value(chart, acc_series_x, acc.x);
lv_chart_set_next_value(chart, acc_series_y, acc.y);
lv_chart_set_next_value(chart, acc_series_z, acc.z);
}
if (qmi.getGyroscope(gyr.x, gyr.y, gyr.z)) {
USBSerial.print("{GYRO: ");
USBSerial.print(gyr.x);
USBSerial.print(",");
USBSerial.print(gyr.y);
USBSerial.print(",");
USBSerial.print(gyr.z);
USBSerial.println("}");
}
}
delay(20); // Increase the frequency of data polling
}
代码解释
-
my_disp_flush():- 这个函数是 LVGL 显示驱动的刷新函数。它负责将 LVGL 的绘图缓冲区内容刷新到显示屏上;
- 根据不同的颜色格式设置,调用
gfx对象的相应函数来绘制位图到特定的区域; - 最后通知 LVGL 显示刷新已完成。
-
loop():- 调用
lv_timer_handler让 LVGL 处理图形界面的任务; - 检查
qmi(QMI8658 传感器对象)是否有新数据准备好。如果有,尝试获取加速度数据和陀螺仪数据,并通过串口输出; - 同时,将加速度数据更新到 LVGL 的图表上,以便实时显示加速度在三个轴上的变化情况;
- 通过
delay(20)增加数据轮询的频率,以确保及时获取传感器数据并更新显示。
- 调用
11_LVGL_Arduino
本示例演示了 LVGL Widgets 示例,动态状态下帧率可达 20~30 帧

